Broad-Based Capital Injections
Japan’s Act on Strengthening Financial Functions (ASFF)
Purpose
“In an environment where financial institutions had difficulty in securing financing on their own, provide sufficient funding through capital participation via public fund injection so that the financial sector can voluntarily commit to risk taking and function as financial intermediaries in the regional economy.” (Endo 2013)
Key Terms
-
Announcement DateJune 14, 2004
-
Operational DateAugust 1, 2004
-
Date of First IssuanceSeptember 2006
-
Program EndMarch 2026 (after the amendment in June 2020)
-
Program SizeOriginally ¥2 trillion, now expanded to ¥15 trillion after the amendment in June 2020
-
Eligible InstitutionsBanks and designated nonbanks
-
AdministratorThe Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan (DICJ) Resolution and Collection Corporation of Japan (RCC, the subsidiary of the DICJ)
-
Legal AuthorityPassed through the Japanese Diet, executed by the Prime Minister’s Office
-
Notable FeaturesSME lending focus, merger and acquisitions focus (after May 2021 amendment), multiple amendments with end date extensions, size expansions, and more generous debt restructuring requirements
After the Japanese Financial Crisis in 1990s, the non-performing loan problem was mitigated in the large Japanese banks but persisted in the regional banking system. By 2004, regional banks accounted for half of all non-performing loans. In 2004, the government passed the Act on Strengthening Financial Functions (ASFF)FThe Act on Strengthening Financial Functions is also referred to in Japanese financial crisis literature and government documents as Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Function, or Financial Functions Strengthening Act, and written as 金融機能強化法 (Kinyuukinoukyokahou) in Japanese., legislation for capital injections to address the non-performing loan problem. Aimed at regional banks, the ASFF secured ¥2 trillion in capital, with various eligibility restrictions and requirements, such as a rigorous debt restructuring plan. As the Japanese economy and the financial system encountered multiple external shocks, the government amended the Act several times. Following the shocks, including the Global Financial Crisis in 2008, the Great East Earthquake in 2011, Brexit in 2016, the COVID-19 outbreak of 2020, and the COVID-19 recession in 2021, the government expanded the ASFF’s scale, extended end dates, and relaxed eligibility and debt restructuring requirements. The ASFF—originally established to recover the capital adequacy ratios for banks—eventually turned into a macroprudential tool through amendments that made the application more accommodative (Sakaguchi 2020, 3). In total, by the end of September 2020, over 30 financial institutions applied and received ¥684.04 billion in capital injections in the form of preferred shares, subordinated loans and debt, preferred investments, and trust beneficiary rights. ¥200.5 billion in capital has been recovered to date (DICJ 2020a, 62–63).
|
Japan Context 2004 - 2006 |
|
|
GDP (SAAR, nominal GDP in LCU converted to USD) |
$5.02 trillion in 2004 $4.56 trillion in 2005 $4.58 trillion in 2006 |
|
GDP per capita (SAAR, nominal GDP in LCU converted to USD) |
$37,689 in 2004 $37,218 in 2005 $35,434 in 2006 |
|
Sovereign credit rating (Five-year senior debt) |
Data for Q4 2004: Fitch: AA- Moody’s: A2 S&P: AA-
Data for Q4 2005: Fitch: AA- Moody’s: A2 S&P: AA-
Data for Q4 2006: Fitch: AA- Moody’s: A2 S&P: AA- |
|
Size of banking system |
$7.37 trillion in 2004 $6.77 trillion in 2005 $6.93 trillion in 2006 |
|
Size of banking system as a percentage of GDP |
146.8% in 2004 148.5% in 2005 151.2% in 2006 |
|
Size of banking system as a percentage of financial system |
46.9% in 2004 47.7% in 2005 50.0% in 2006 |
|
Five-bank concentration of banking system |
52.4% in 2004 51.9% in 2005 51.4% in 2006 |
|
Foreign involvement in banking system |
Data not available for 2004–06 |
|
Government ownership of banking system |
Data not available for 2004–06 |
|
Existence of deposit insurance |
Yes in 2004–06
|
|
Sources: Bloomberg, World Bank Global Financial Development Database, World Bank Deposit Insurance Dataset. |
Following the Japanese financial crisis in the late 1990s, the Japanese government introduced a number of crisis-fighting tools and adopted restructuring frameworks. In 2002, the disposal of bad loans became a priority for the Japanese government under Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi (Koizumi 2002). Former chair of the Financial Reconstruction Committee Hakuo Yanagisawa had chaired the Japanese Financial Services Agency (JFSA) until that point but was dismissed because of lack of progress in resolving the non-performing loan (NPL) problem. Yanagisawa was replaced by Heizo Takenaka, who enforced what came to be known as the Takenaka Plan, one of the most controversial financial policies adopted in Japan (Himino 2021). While the details of the Takenaka Plan did not differ significantly from the previous plan, it was characterized by stricter enforcement of restructuring policies (Hoshi and Ito 2004). Under Takenaka, many big banks improved their capital ratios and stock prices increased (Hoshi and Kashyap 2010; Himino 2021).
However, while large city banks improved their capital ratios, regional banks lagged in disposing of nonperforming loans (IMF 2004). Regional banks were exempted from the government policy requiring a halving of the NPL ratio (Koizumi 2002). As of March 2003, Barclays estimated regional banks accounted for 54 percent of system-wide NPLs, amounting to ¥23.8 trillion. By January 2004, the Japanese government determined regional banks to be a priority for financial stability (Hirano 2004).
In January 2004, in response to the burgeoning NPL problem within the regional banks, the Prime Minister’s Cabinet submitted the Act on Strengthening Financial Functions (ASFF) to the Japanese Diet, earmarking ¥2 trillion for public capital injections into regional banks (House of Representatives, Japan 2004). FSA Chair Heizo Tanaka commented that regional banks would be inspected as strictly as national banks under previous public capital injections (Hirano 2004). The bill was discussed between January and June, and on June 14, 2004, the Japanese Diet passed the bill, two days before the end of the 159th Diet Session (House of Representatives, Japan 2004). The amount, price, capital characteristics, and the timing of the capital injection under the ASFF varied across financial institutions, tailored to each institution’s needs.
Following the original legislation in 2004, the government made a series of amendments to the legislation to utilize the capital injection framework for various purposes.
First, in September 2008, the collapse of Lehman Brothers created the impetus to pass legislation to support the Japanese economy. Then Prime Minister Aso announced the Comprehensive Immediate Policy Package to Ease Public Anxiety (Aso 2008). The package focused on improving small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) financing, with a series of policy measures intended to improve economic well-being with several fiscal targets (Endo 2013). Under these measures, the Diet passed the first amendment to the ASFF, relaxing some eligibility and debt restructuring requirements, extending the sunset date from the end of March 2008 to March 2012, and expanding the size from ¥2 trillion to ¥12 trillion (FSA 2008).
Second, in March 2011, an earthquake of unprecedented scale—9.0 in magnitude—struck the northern coast of Japan. Immediately following, the Prime Minister’s office added line items to the supplementary budget for disaster relief efforts (Noda 2011). Four months later, the Diet passed an amendment to the existing recapitalization legislation with special clauses for regional institutions supporting the revitalization of areas affected by the earthquake and extended the sunset date to the end of the March 2017 (House of Representatives, Japan 2011; Endo 2013).
Third, in 2016, Japan held the presidency of the G7 countries. During this presidency, the UK public voted to leave the EU. To show leadership, the Japanese government led the G7 in preparing for potential financial stability implications resulting from Brexit. The government proposed another amendment to the act to prepare for the risks arising from Brexit by continuing to support the growth of SMEs; this time the government amended the sunset date to the end of March 2022. The amended bill passed the diet on December 2, 2016 (Abe 2016; House of Representatives, Japan 2016).
Fourth, in 2020, upon the outbreak of the global COVID-19 pandemic, the Japanese Diet passed another amendment to the ASFF. On June 13, the Diet extended the period of public capital injections to financial institutions for an additional four years, to the end of 2026. The amended bill also proposed the expansion of the available public funds for the injection from ¥12 trillion to ¥15 trillion (House of Representatives, Japan 2020). In proposing the new amendment, Taro Aso, the Minister of State for Financial Services emphasized that the domestic financial system was sound and that the amendment was a preemptive measure ensuring the long-run soundness of the financial system so that it could continue to support SMEs impacted by the COVID-19 crisis and revitalize the economy (Aso 2020).
The fifth and most recent amendment to the ASFF was passed by the Diet on March 5, 2021 and was implemented on May 19, 2021. The Japanese Diet explained that the purpose of the amendment was to maintain financial functions that support the recovery and revitalization of regional economies (rural areas) in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic. Citing declining populations in those regional areas, regional banks that plan to merge or acquire other banks may submit "implementation plans” to receive capital injections (FSA 2021). The declining population and its negative impact on regional economies and the financial system have long been a concern for Japan. For instance, the Bank of Japan’s April 2017 Financial System Report raised concerns about declining profitability of financial institutions, noting that the consequences of a declining population and other macro factors could lead to potential vulnerabilities (Bank of Japan 2017). In November 2020, the Bank of Japan also introduced the “Special Deposit Facility to Enhance the Resilience of the Regional Financial System,” a program to promote cost savings, mergers, and other acquisitions within regional banks (Bank of Japan 2020).
Figure 1 below summarizes the evolution of ASFF and participation data.
Figure 1: Evolution of the Act on Strengthening Financial Functions


 Source: Sakaguchi 2020; FSA 2021; 2008; 2011b; House of Representatives, Japan 2004; 2011; 2020.
Source: Sakaguchi 2020; FSA 2021; 2008; 2011b; House of Representatives, Japan 2004; 2011; 2020.
Summary Evaluation
Though the program became operational on August 1, 2004, it remained unutilized until two years later, when Kiyo Bank and Howa Bank became the first banks to apply for injection in August 2006. The banks received capital in in November and December of 2006, respectively. The banks requested ¥39 billion total, with Kiyo bank requesting ¥30 billion and Howa Bank requesting ¥9 billion. They eventually received ¥40.5 billion, with Kiyo Bank receiving an additional ¥1.5 billion more than requested (DICJ 2020b).
After the amendment to the ASFF in 2008, 11 additional financial institutions participated the scheme, receiving a total of ¥309 billion. After a second amendment in 2011, which also extended the application period, an additional 21 institutions participated in the injection, receiving ¥309.1 billion (of which 13 financial institutions were designated as “Great East Japan Earthquake impacted financial institutions”). In December 2016, the Japanese government extended of the application period again, through March 31, 2022. Since December 2016, two institutions have applied, receiving ¥16.24 billion yen. The evolution of the law and its utilization can be seen above in Figure 1.
Thirty institutions participated in the capital injection scheme, with some institutions participating multiple times. As of the end of September 2020, the Japanese government had ¥684.04 billion capital injected, and ¥200.5 billion has been repaid so far, leaving ¥483.54 billion the remaining balance. (See Figure 2 below.) (DICJ 2020b).
Figure 2: ASFF Cumulative Injections and Repurchases

Source: Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan n.d.
Of financial institutions that participated in the capital injection program, five have repaid or repurchased shares either partially or in full (77 Bank, Kiyo Bank, Howa Bank, North Pacific Bank, and Kirayaka Bank). Both Howa Bank and Kiyo Bank repurchased their preferred shares within 10 years of the capital injection. Under the extension made during the Lehman Brothers bankruptcy, two of the remaining 28 banks, North Pacific Bank and Kirayaka Bank, repurchased their preferred shares. Only one bank in the subsequent extensions, 77 Bank, has repaid the amount injected. (See Figure 3).
There is still a substantial amount of capital outstanding from the series of capital injections. The capital injection framework was utilized most during the Global Financial Crisis and in the aftermath of the Great East Japan earthquake. The Fukushima region has seen an economic recovery, but it is unclear the extent to which the regional banking sector played a role. Similarly, while banks have utilized the legislation after the amendment concerning Brexit was passed, it has been unclear the repercussions Brexit will have on financial stability and regional banking needs, and so far no banks have applied the capital injection since the COVID-19 2020 amendment.
Figure 3: Repayment Status
 Source: Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan n.d.
Source: Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan n.d.
The original Act on Strengthening Financial Functions (ASFF) was passed as a stand-alone package, without any other accompanying legislation (Hirano 2004; House of Representatives, Japan 2004).FSome consider the ASFF as part of the Program for Financial Revival or the Financial Reconstruction Program, a framework established in October 2002 to reduce non-performing loans (Matsubayashi 2015, 20; Endo 2013). In July 2003, a public discussion paper on the public capital injection scheme was published, and the ASFF was eventually designed under the discussed frameworks (Oomori 2017, 3–4; Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee 2003). Meanwhile, it can be regarded as one of the components in the series of broad-based capital injections throughout the Japanese financial crisis. As shown in Figures 4 and 5, the Financial Function Stabilization Act and the Prompt Recapitalization Act in 1998 were the two broad-based capital injection frameworks that preceded the ASFF.
Figure 4: Timeline of YPFS Japanese Broad-Based Capital Injection Cases
 Source: Authors’ analysis.
Source: Authors’ analysis.
Figure 5: Summary and Timeline of Japanese Capital Injection Frameworks

 Source: Authors’ analysis.
Source: Authors’ analysis.
Key Design Decisions
Part of a Package
1
Subsequent amendments were sometimes packed with other economic or financial policies. For instance, the amendment in 2008 corresponded with economic policies at the Enterprise Turnaround Initiative Corporation of Japan and the SME Revitalization Support Councils (Hatanaka 2012; Endo 2013). Furthermore, the JFSA and media often emphasized the coordination of the COVID-19 related ASFF 2020 amendment and the Special Act under the Anti-Trust Law (FSA 2020). Lastly, the most recent amendment in June 2021 was paired with revisions in other laws; one banking law revision eased restrictions on the scope of bank's business and equity investments, and another investment law was intended to promote overseas investors’ participation in Japanese financial markets (Jiji Press 2021).
Legal Authority
1
In January 2004, in response to the burgeoning nonperforming loan issue at regional banks, the Prime Minister’s Cabinet submitted the Act on Strengthening Financial Functions to the Japanese Diet, earmarking ¥2 trillion for public capital injections into regional banks. On June 14, 2004, the Japanese Diet finally passed the bill, two days before the end of the 159th Diet Session (House of Representatives, Japan 2004). Each subsequent amendment passed through the Diet successfully as well.
Communication
1
The Prime Minister’s office publicly announced each recapitalization bill and the subsequent amendments. The Diet debated each bill and amendment publicly before officially passing them. Occasionally, the Minister of State for Financial Service also released official statements.
Governance
1
Multiple stakeholders are involved in the ASFF capital injection scheme, including ministers from relevant ministries, prime minister, the Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee (Committee), and the DICJ.
The Japanese Financial Services Agency (JFSA), under the Ministry of Finance, was tasked to form the CommitteeFThis committee has also been referred to as the “Banking Function Reinforcement Study Council” and the “Examination Committee for Strengthening Financial Functions”, referred as 金融機能強化審査会 (Kinyuukinoukyoukashinsakai) in Japanese. to assess applications and oversee the implementation of the plans for the recapitalization (House of Representatives, Japan 2004, 48). The Committee consisted of part-time members appointed by the prime minister serving three-year terms (House of Representatives, Japan 2004, 49,51). The maximum number of members is 6 people (The House of Representatives, Japan 2021). The JFSA website hosts the Committee’s meeting minutes soon after the meeting and transcripts are publicly disclosed three years after meetings (Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee 2004, 5). As of June 2021, according to the JFSA website, the Committee has met 25 times over the span of the ongoing recapitalization (Financial Service Agency, n.d.).
The Committee evaluates the management enhancement plan submitted by the applicant financial institutions. The involved ministers—including the Commissioner of JFSA or the Minister of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, depending on the type of the financial institution, the Minister of Finance, and prime minister—receive reports. The ministers also have the right to approve or request exercise rights, including conversions. Voting rights are only exercised if the banks with preferred shares do not pay their dividends (see Key Design Decision #11 for further detail) (Sakaguchi 2020).FSo far, Howa Bank (received capital in December 2006) has been the only bank that borrowed capital in preferred shares with voting rights to appoint or dismiss directors (DICJ 2020b).
The DICJ entrusts the operation of capital participation, management, and disposal to the RCC, a subsidiary of the DICJ. The RCCFFor more information regarding the RCC and its operations, please refer to the “Resolution and Collection Corporation” YPFS case study (Dreyer 2021). was created as a merger between the Housing Loan Administration Corporation and the Resolution and Collection Bank on April 1, 1999, under the Financial Revitalization Act. The RCC is funded entirely by the DICJ (DICJ 2020a). The DICJ acts independently of the Bank of Japan or the Treasury, though in close cooperation (Financial Stability Board 2016).
The RCC has been responsible for managing capital and making purchases as determined by the Committee. Funded by the DICJ, the RCC purchased either preferred stocks, subordinated bonds and debt, preferred investments, or trust beneficiary rights from the financial institutions that applied for capital injections under the ASFF (Hoshi and Kashyap 2010).
The actual capital injection operations vary based on the characteristics of the financial institutions applying for the injection. For instance, the support for financial institutions undergoing restructuring is different than that of institutions that are not undergoing restructuring. Also, non-banks (e.g., cooperative structured central financial institutions) and banks that are affected by earthquakes or COVID-19 receive a different treatment in application, screening, and funding (DICJ 2020a).
Program Size
1
When the ASFF was passed in June 2004, the DICJ's Financial Functions Strengthening Account had a budget of ¥2 trillion. As the Act was amended over the years, the size expanded to ¥15 trillion. So far, as of the end of September 2020, the Japanese government had utilized ¥684.04 billion in capital, only 4.5% of the full capacity (DICJ 2020b).
Timing
1
Unlike the Prompt Recapitalization Act or other past capital injection frameworks, each financial institution received their capital on their own application timeframe, and there was no coordinated schedule across the various financial institutions. Each financial institution received capital once its application (including the management plan) had been screened by the Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee and accepted by the Japanese government.
Source of Injections
1
The DICJ holds the Financial Functions Strengthening Account, which is specifically dedicated for the ASFF. Under Article 29, paragraph (1) of the ASFF Act, the DICJ’s Financial Functions Strengthening Account is funded through the issuance of government-backed DICJ bonds and borrowings from financial institutions, other investors, and in rare instances, directly from the Bank of Japan (Financial Stability Board 2016; DICJ 2020a). Under Article 45 of the ASFF, the government guarantees the account (Financial Stability Board 2016; DICJ 2020a).FDICJ bond issuances and borrowings are subject to ceilings set out in the Deposit Insurance Act and are complemented by annual budgetary appropriations (as approved by the Diet) for the amount guaranteed by the government. (Financial Stability Board 2016). The government guarantee ceiling was ¥12 trillion in the budget for fiscal year 2020 and ¥15 trillion for the second supplementary budget for fiscal year 2020 (DICJ 2020a). The extent to which DICJ funded the ASFF recapitalization from either source is shown in Figure 6 below.
Figure 6: Funding Status of the Financial Functions Strengthening Account
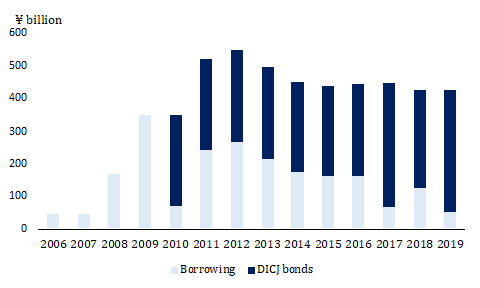 Note: Years in Japanese fiscal year (April – March next year).
Note: Years in Japanese fiscal year (April – March next year).
Source: DICJ 2020a.
Meanwhile, the funding source for financial institutions that undergo mergers and management integration under the ASFF capital injection scheme introduced in May 2021 is slightly different. The revised ASFF now provides approximately a third of the initial cost of system integration and branch consolidation, accounting for about ¥3 billion (Nikkei 2021; Jiji Press 2021).
Eligible Institutions
1
Unlike some of the previous recapitalizations, the ASFF did not require financial institutions to be of systemic importance to receive capital injections using public funds. The Committee accepts applications from financial institutions that fail to fulfill the capital adequacy requirements (but are not bankrupt or insolvent) or financial institutions that meet the capital adequacy requirements but intend to undertake a fundamental organizational restructuring (Ikenaga and Watanabe 2008).
Any domestic or foreign bank was eligible for capital injection; however, no foreign banks participated (Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan 2020b).
The law did not require the participation of any banks, and the application was voluntarily. It did allow the participation of specific non-banks, listed explicitly: Norinchukin Bank, the Long-Term Credit Bank, the Federation of Agricultural Cooperatives, Fisheries Cooperative Association, and the Federation of Fisheries Processing Cooperatives. The law also allowed the participation of shinkin banks, labor unions, credit cooperatives (shinkumi), and bank holding companies (House of Representatives, Japan 2004).FThe amendment of 2008 newly created an injection scheme for the Central Organization of Cooperative Structured Financial Institution, enabling easier access to capital support to each non-banks as well as reinforcing the financial soundness of the for the Central Organization of Cooperative Structured Financial Institution (Ikenaga and Watanabe 2008).
Furthermore, after the amendment in 2008, the focus on SMEs in the regional economy intensified (Ikenaga and Watanabe 2008). After the collapse of the Lehman Brothers on September 15, 2008, the Japanese government proposed the Comprehensive Immediate Policy Package to Ease Public Anxiety, with fears over how global economic events might lead to a credit crunch for SMEs (Aso 2008; Yamori et al. 2013). In the new iteration of the program, the facilitation of credit to SMEs became a special focus in management plans submitted. The amendment extended the period for application from March 31, 2008 to March 31, 2012.
Following the Great East Japan Earthquake, the Diet passed an amendment to the existing recapitalization legislation with special clauses for regional institutions supporting the revitalization of areas affected by the earthquake (FSA 2011a). In this amendment, the Japanese government extended the application period for capital injections, in addition to creating special treatment for those institutions impacted by the Great East Japan Earthquake. Similarly, the June 2020 amendment established special treatment for financial institutions that were affected by COVID-19.
The affected institution can apply for a capital injection without being screened for the feasibility of the targets in the management plan or feasibility of repayment within 15 years (Rhee and Unnava 2020). Affected institutions are those whose “financial statements have gotten considerably worse due to the coronavirus or measures to prevent coronavirus, or if the financial institution needs to lend to companies that are affected by coronavirus or measures to prevent coronavirus” (Rhee and Unnava 2020). Sakaguchi (2020) assumes that eventually all financial institutions should fall under these criteria.
Lastly, the 2021 amendment related to COVID-19 covers approximately one-third of initial costs related to business integration, including system and branch consolidations for those financial institutions undergoing mergers and organizational restructuring (Jiji Press 2021). While the promotion of mergers and reorganization is similar the Organizational Restructuring Act (a capital injection scheme that was established in December 2002), financial institutions can apply for the capital injection even when their capital adequacy ratios are above the requirement. According to the revised Act, financial institutions that wish to receive capital for system and branch consolidations will submit an “implementation plan,” indicating their outlook for the reorganization and contribution to the regional economy (The House of Representatives, Japan 2021).
Individual Participation Limits
1
No explicit statement limiting individual participation was found in the legal documents. As of September 2020, the largest capital injected was ¥100 billion (North Pacific Bank in March 2009), and the mean and median of the capital received were ¥18.5 billion and ¥15 billion, respectively (DICJ 2020b).
Capital Characteristics
1
The capital characteristics and terms were decided on a case-by-case basis (DICJ 2020b). Ultimately, the Committee utilized a combination of preferred shares, subordinated debt, priority investment, and trust beneficiary rights for capital injections over the multiple injection windows.
So far, 18 banks received capital in the form of convertible preferred shares, 13 non-banks in trust beneficial rights, five non-banks in preferred investments, and one bank in the form of a subordinated loan (DICJ 2020b). No financial institution has received in capital support in the form of common shares, though it is an option if the financial institution’s capital ratio is below the regulatory requirement (Aso 2008; House of Representatives, Japan 2004; FSA 2008; House of Representatives, Japan 2011; 2016; Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan 2020a). A detailed table listing of the characteristics and the terms for capital is available in the Appendix.
Other Conditions
2
Applicant institutions proposed terms via their management plans, which were then considered by the Committee (Financial Service Agency, n.d.; House of Representatives, Japan 2004). A detailed table listing of the characteristics and the terms for capital is available in the Appendix.
It appears that financial institutions proposed granular terms in their plans—including repayment dates, dividend rates, and instruments to be used for injection—which were then reviewed by the Committee. These terms were presented to members in the Committee meetings and then approved or rejected. There appear to have been no rejections of financial institution applications at any point, including the revisions to management plans after the plan periods ended.
Management plans were evaluated along several criteria, listed in Figure 7 below.
Figure 7: Evaluation Criteria for Management Enhancement Plans
 Source: FSA, n.d.
Source: FSA, n.d.
The requisite information on underwriting terms were also evaluated, shown below in Figure 8.
Figure 8: Evaluation Strategy for Proposed Share Underwriting.
 Source: FSA, n.d.
Source: FSA, n.d.
The application also required banks to submit their capital status, as well as balance sheet information, for evaluation. While the Committee did not explicitly require increased SME lending as part of the original application for capital injection, the Committee evaluated the plans against this criterion before the amendment to the legislation in 2008 (FSA, n.d.; House of Representatives, Japan 2004).
These requirements for management plans and capital status were radically eased after several amendments (Figure 1). For instance, management responsibility is no longer strictly pursued after the 2008 amendment. Furthermore, in the 2011 amendment, the government introduced multiple exemptions of requirements for financial institutions that were affected by the Great East Earthquake. Such exemptions included the requirement to set numerical targets and establish a responsible management system. After the 2020 amendment, these exemptions from the requirements eventually expanded to COVID-19 affected financial institutions (which are assumed to be all financial institutions, according to Sakaguchi 2020).
As seen in the Appendix, preferred shares had mandatory conversion dates to common shares, while trust rights ranged in period from 10 to 25 years, though the terms were potentially extendable (DICJ 2020b). The beginning of the conversion period for the convertible preferred shares also varied from bank to bank, sometimes as early as within a month (e.g., Kirayaka Bank and Howa Bank), or more than seven years after the capital injection (Michinoku Bank) (DICJ 2020b).
After the capital injection, the conversion price is often calculated as the average of the common equity (stock) price over the week preceding the calculation. The conversion price on convertible preferred shares has a “floor price.” The floor price is often calculated as 50% of the average price of common stock when the capital was injected to the targeted financial institution. There is no “ceiling” price in the convertible preferred shares (Sakaguchi 2020).
After the 2008 amendment, financial institutions were given the option to buy the preferred stock at book value, the equivalent to providing a call option for financial institutions. This option can be exercised if the stock price continuously falls under the conversion price and if banks request the JFSA to do so. Sakaguchi (2020) notes that the stock prices of many of the banks affected by the Great Earthquake fall under the floor price.FThis is not only because the stock price of the Great Earthquake affected banks hover low, but also because the floor price of those banks was arbitrarily set higher compared to non-affected banks (Sakaguchi 2020, 9). The floor price adjustment is not mentioned in the ASFF Act legal text but rather implemented on the ad-hoc capital design basis. Sakaguchi (2020) warns that the higher floor price may be functioning as the permanent subsidies for certain banks, narrowing the exit of the program.
For preferred investments, so far, all the receivers have been Shinkumi Federation banks, in the form of preferred perpetual investments (noncumulative corporate bonds). In terms of trust beneficial rights, the trust period has been either 10 or 25 years, which is can also be extendable. For those with 10 year trust periods, it is stipulated that within 10 years following the capital injection, either “authorization of management improvement” or “authorization of capital reorganization associated with business restructuring” will be obtained (DICJ 2020b).
In terms of capital with voting rights, the DICJ clarifies on its website that it can exercise its rights as a shareholder and investor, considering three factors:
- If it contributes to maintaining the soundness of bank management,
- If it contributes to securing a repayment source of public funds,
- If it is in accordance with the purposes of the law, such as financial facilitating, on which capital injection of public funds has been based (DICJ, n.d.).
In addition, the DICJ pays attention to if its exercise of rights is consistent with administrative policies and measures. However, available information doesn’t clarify to what extent the DICJ or RCC have exercised those rights.
No further detail has been found for this Key Design Decision.
Restructuring Plan
1
There appear to have been no rejections of financial institution applications at any point, including revisions to management plans after plan periods ended.
Each financial institution reports the ongoing status of the management plan, and the JFSA publishes those reports annually on its website. Furthermore, if the management plan were to be revised, they are rescreened and reexamined by the Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee (Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee 2004).
The application also required banks to submit their capitalization status, as well as balance sheet information, for evaluation. While the Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee did not explicitly require increased SME lending as part of the original application for capital injection, the Committee evaluated organizations along this criterion before the amendment to the legislation in 2008 (Financial Service Agency, n.d.; House of Representatives, Japan 2004). However, these requirements in the management plan and capitalization status were radically eased after several amendments (Figure 1). For instance, management responsibility no longer strictly pursued after the 2008 amendment. Furthermore, in 2011 amendment, the government introduced multiple exemptions of requirements for financial institutions that were affected by the Great East Earthquake amendment. Such exemptions included the requirement to set numerical targets and establish a responsible management system. After the 2020 amendment, these exemptions of the requirements eventually expanded to COVID-19 affected financial institutions (which are assumed to be all financial institutions, according to Sakaguchi 2020).
Fate of Existing Board and Management
1
In the original, stricter version of management plans, the government required the highest levels of management to resign upon receipt of capital injection. In addition, external board members were required to be appointed if they were not already part of the board. Later, the government could request members of the board or management to resign only if the financial institution’s capital ratio was below 4% when the institution applied for capital injection.
Exit Strategy
1
Of the banks that participated in the capital injection program, five have repaid or repurchased shares either partially or in full. Both Howa Bank and Kiyo Bank repurchased their preferred shares within ten years of the capital injection. Under the extension made during the Lehman Brothers bankruptcy, two of the remaining 28 banks, North Pacific Bank and Kirayaka Bank, repurchased their preferred shares. Only one bank in the subsequent extensions, 77 Bank, has repaid the amount injected. (See the Appendix). As of the end of September 2020, the Japanese government had ¥684.04 billion capital injected, and ¥200.5 billion has been repaid so far, leaving ¥483.54 billions the remaining balance.
In October 2005, the DICJ published “Immediate Guideline for Disposal of Preferred Stocks, etc. Acquired through Capital Injection with Public Funds” and clarified the criteria for repayment and disposal (DICJ 2005). According to this guideline, the DICJ will dispose the preferred stocks and other capital under the following three situations:
- If the recapitalized financial institution requests the selling of Preferred Stocks to third parties (including sale in the capital market)
- If the recapitalized financial institutions request for repaying the public funds injected
- If disposing is strongly preferable under the given market conditions.
Banks were expected to reacquire their shares within 15 years of purchase. In practice, the mandatory acquisition date for financial institutions varied, with some institutions facing mandatory acquisition dates within ten years and some firms facing mandatory acquisition dates 25 years after injection. Additional variation occurred in trust periods, with some firms receiving ten-year periods and some firms receiving 25-year periods, though all were extendable (DICJ 2020b). For those with ten-year periods, the allocation required they receive an additional approval for management plans. Injection through preferred investments have no explicit exit date, as each preferred investment is a preferred perpetual investment injection.
Key Program Documents
-
(Dreyer 2021) Dreyer, Mallory. 2021. “The Resolution and Collection Corporation of Japan.”
A YPFS case study on the broad-based asset management company in Japan after the 1990s financial crisis.
-
(FSA, n.d.) Financial Service Agency. no date. “金融機能強化審査会.” Financial Service Agency. Accessed June 18, 2021.
A webpage with an overview of the Financial Function Examination Committee and the agendas.
-
(Hatanaka 2012) Hatanaka, Ryutaro. February 10, 2012. “International Conference on ‘Asian Market Integration and Financial Innovation.’”
A speech from the FSA Commissioner on Japanese financial stability measures.
-
(Ikenaga and Watanabe 2008) Ikenaga, Tomoaki, and Masayuki Watanabe. November 2008. “Amendment to Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions.”
A summary of changes to financial institution support under an amendment to the Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions.
-
(Oomori 2017) Oomori, Kengo. February 27, 2017. “金融機関への公的資金投入をめぐる議論,” February 11.
A summary of the 2017 status of public funding and capital injections for Japanese financial institutions.
-
(Rhee and Unnava 2020) Rhee, June, and Vaasavi Unnava. June 19, 2020. “Japan Begins Capital Injections for Financial Institutions in Response to COVID-19.” Yale School of Management (blog).
A blog post summarizing the Japanese government’s support for financial institutions in response to Covid-19.
-
(Sakaguchi 2020) Sakaguchi, Junya. July 30, 2020. “改正金融機能強化法のコロナ特例措置がもたらす功罪.”
A summary of the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on a law regarding financial institutions.
-
(Unnava 2021a) Unnava, Vaasavi. November 12, 2021. “Financial Functions Stabilization Act.” Journal of Financial Crises.
YPFS case study examining the Financial Functions Stabilization Act.
-
(Unnava 2021b) Unnava, Vaasavi. November 12, 2021. “Prompt Recapitalization Act.” Journal of Financial Crises.
YPFS case examining the Prompt Recapitalization Act.
-
(DICJ 2005) Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan. October 2005. “Immediate Guideline for Disposal of Preferred Stocks, Etc. Acquired through Capital Injection with Public Funds.” Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan.
Guidelines from the DICJ regarding the disposal of preferred stocks and subordinated bonds as part of the recapitalization by the RCC.
-
(DICJ 2020b) Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan. September 2020. “Capital Participation Operations Pursuant to the Financial Functions Strengthening Act: Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan.” Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan.
Operational details of the recapitalizations under the Act.
-
(Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan, n.d.) Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan. no date. “Basic Policy in Exercising a Voting Right as a Shareholder.” Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan. Accessed June 17, 2021.
An outline of how the DICJ examines its role in exercising its voting rights as a shareholder.
-
(Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee 2003) Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee. July 2003. “金融機関に対する公的資金制度のあり方について.”
A document outlining funding and support of financial institutions in Japan.
-
(FSA 2011a) Financial Service Agency. May 2011. “金融機能強化法等の改正に係る説明資料.” May.
A presentation providing additional guidance on the amendments to the act.
-
(FSA 2008) Financial Service Agency. December 16, 2008. “「金融機能の強化のための特別措置に関する法律施行令の一部を改正する政令」及び「金融機能の強化のための特別措置に関する内閣府令の一部を改正する内閣府令」等について:金融庁.”
A document outlining the cabinet amendments to acts allowing support to financial institutions.
-
(FSA 2021) Financial Service Agency. May 28, 2021. “令和3年金融機能強化法改正に係る政令・内閣府令案等の公表について.”
A website listing the amendments to the act in 2021.
-
(House of Representatives, Japan 2004) House of Representatives, Japan. June 18, 2004. 金融機能の強化のための特別措置に関する法律.
The text of the Law Concerning Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions.
-
(House of Representatives, Japan 2011) House of Representatives, Japan. June 29, 2011. 東日本大震災に対処して金融機関等の経営基盤の充実を図るための金融機能の強化のための特別措置に関する法律及び金融機関等の組織再編成の促進に関する特別措置法の一部を改正する法律.
The text of a bill that revised the Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions in 2011.
-
(House of Representatives, Japan 2016) House of Representatives, Japan. December 2, 2016. 金融資本市場をめぐる情勢の変化に対応して金融の機能の安定を確保するための金融機能の強化のための特別措置に関する法律等の一部を改正する法律案.
The text of the bill that revised the Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions in 2016.
-
(House of Representatives, Japan 2020) House of Representatives, Japan. June 18, 2020. 金融機能の強化のための特別措置に関する法律.
The text of the Law on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Institutions of 2020.
-
(The House of Representatives, Japan 2021) The House of Representatives, Japan. May 2021. 金融機能強化のための特別措置に関する法律施行令改正案.
An amendment to the to the act in 2021.
-
(Abe 2016) Abe, Shinzo. September 26, 2016. “Policy Speech by Prime Minister to the 192th Session of the Diet.”
A speech by the Prime Minister to the Diet in 2016.
-
(Aso 2008) Aso, Taro. September 29, 2008. “Policy Speech by Prime Minister Taro Aso to the 170th Session of the Diet.”
A speech by the Prime Minister to the Diet in 2008.
-
Aso 2020) Aso, Taro. May 27, 2020. “Amendment to the ‘Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions’ (Statement by ASO Taro, Minister of State for Financial Services).”
A statement on the impact of Covid-19 and how the government amended the Act to respond to the pandemic.
-
(Bank of Japan 2020) Bank of Japan. November 10, 2020. “Introduction of ‘Special Deposit Facility to Enhance the Resilience of the Regional Financial System.’”
A press release announcing the establishment of a special facility in response to the Covid-19 crisis.
-
(FSA 2020) Financial Service Agency. August 2020. “Fight against COVID-19 and Develop a Better Post-COVID Society.”
A letter from the FSA outlining its priorities.
-
(Koizumi 2002) Koizumi, Junichiro. October 30, 2002. “Statement by Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi (Regarding Comprehensive Measures to Accelerate Reform).”
A speech by the prime minister regarding the financial reform measures.
-
(Noda 2011) Noda, Yoshihiko. April 28, 2011. “Speech on Fiscal Policy by Minister of Finance Noda at the 177th Session of the National Diet.” Japan Ministry of Finance.
Speech on Fiscal Policy by Minister of Finance Noda at the 177th Session of the National Diet.
-
A Japan Times article on the shift from bad loan cleanup to profitability among banks.
A Japan Times article on the shift from bad loan cleanup to profitability among banks.
-
(Jiji Press 2021) Jiji Press. May 19, 2021. “Japan Passes Bill to Spur Regional Bank Realignments.” Jiji Press.
A news article on the Covid-19 related support for regional economies.
-
(Endo 2013) Endo, Toshihide. March 8, 2013. “Post-Crisis Regulation of Financial Institutions in Japan.” Presented at the ADBI-JFSA Joint Conference, March 8.
A presentation regarding the evolution of financial regulation after the Japanese and global financial crises.
-
(Himino 2021) Himino, Ryozo. 2021. The Japanese Banking Crisis. Singapore: Springer Singapore.
A book providing analysis on the Japanese banking crises of the 1990s.
-
(Hoshi and Ito 2004) Hoshi, Takeo, and Takatoshi Ito. December 2004. “Financial Regulation in Japan: A Sixth Year Review of the Financial Services Agency.” Journal of Financial Stability 1 (2): 229–43.
The paper provides a critical review of the Financial Services Agency (FSA) of Japan since its establishment in June 1998 (as the Financial Supervisory Agency) to June 2004.
-
(Hoshi and Kashyap 2010) Hoshi, Takeo, and Anil K Kashyap. 2010. “Will the U.S. Bank Recapitalization Succeed? Eight Lessons from Japan.” Journal of Financial Economics 97 (3): 398–417.
A research paper analyzing the US response to the Global Financial Crisis applying lessons from the Japanese financial crisis.
-
(Matsubayashi 2015) Matsubayashi, Yoichi. March 2015. “The Effort to Stabilise the Financial System in Japan: An Outline and the Characteristics of the Programme for Financial Revival.”
A working paper examining the Program for Financial Revival in Japan and its impact on financial stability.
-
(Yamori, Kondo, Tomimura, Shindo, and Takuku 2013) Yamori, Nobuyoshi, Kazumine Kondo, Kei Tomimura, Yuko Shindo, and Kenya Takuku. 2013. “Japanese Banking Regulations and SME Finance under the Global Financial Crisis.” Japanese Journal of Monetary and Financial Economics 1 (1): 50–90.
A paper that discusses important policy actions in Japanese banking regulation under the global financial crisis.
-
(Bank of Japan 2017) Bank of Japan. April 2017. “Financial System Report.”
The BOJ’s financial sector report for 2017.
-
(DICJ 2020a) Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan. August 2020. “Annual Report 2019/2020.”
The 2019-2020 annual report from the DICJ.
-
(Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee 2004) Financial Function Enhancement Examination Committee. August 2004. “金融機能強化審査会議事録.”
The meeting minutes from a 2004 meeting of an FSA committee.
-
(Financial Stability Board 2016) Financial Stability Board. December 21, 2016. “Peer Review of Japan.”
A review from the FSB of the financial system, macroprudential, and financial stability frameworks.
-
(IMF 2004) International Monetary Fund. April 2004. “Global Financial Stability Report Market Developments and Issues Chapter II Global Financial Market Developments.” International Monetary Fund.
An excerpt from the 2004 IMF Financial Stability Report.
Appendix A: Details of the Preferred Shares (convertibles)


Appendix B: Preferred Investments

Appendix C: Subordinated Loan (10 years three months)

Appendix D: Trust Beneficial Rights




Taxonomy
Intervention Categories:
- Broad-Based Capital Injections
Countries and Regions:
- Japan
Crises:
- Japanese Crisis 1990s